The trusted data resource for craniofacial researchers worldwide
FaceBase is a
collaborative NIDCR-funded project
.
FaceBase Data Summary
New to FaceBase?
Start here for helpful links and guided resources.
Using FaceBase
Contributing data to FaceBase
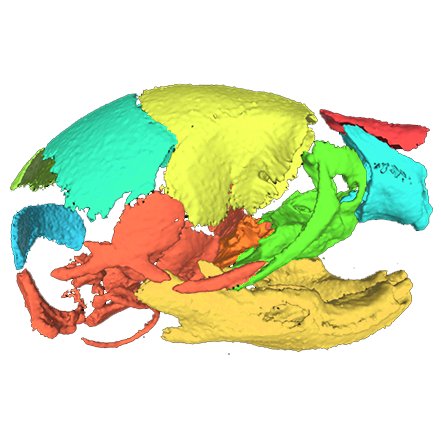
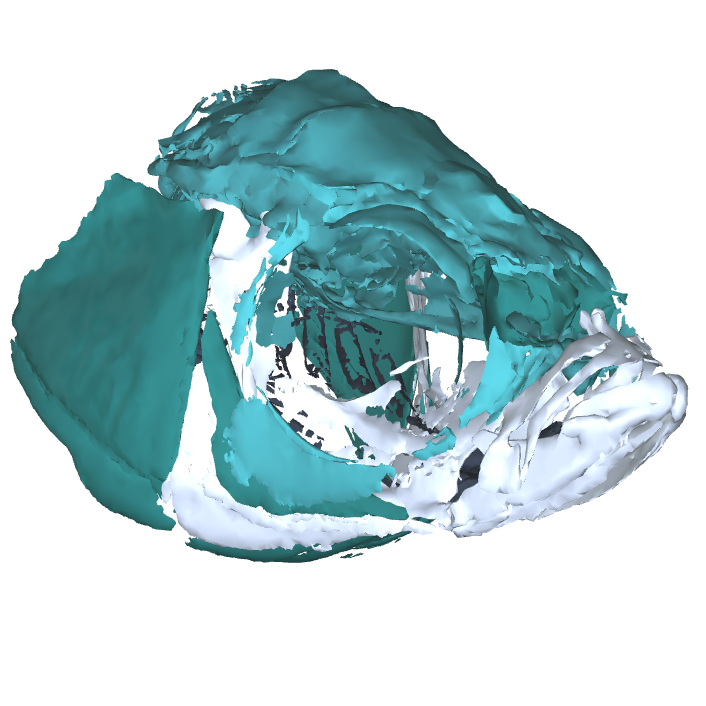
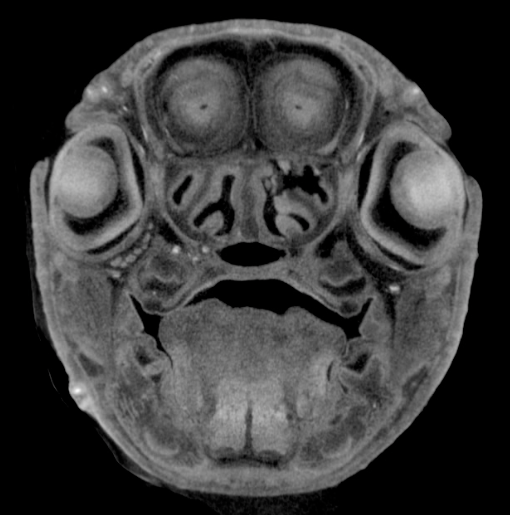
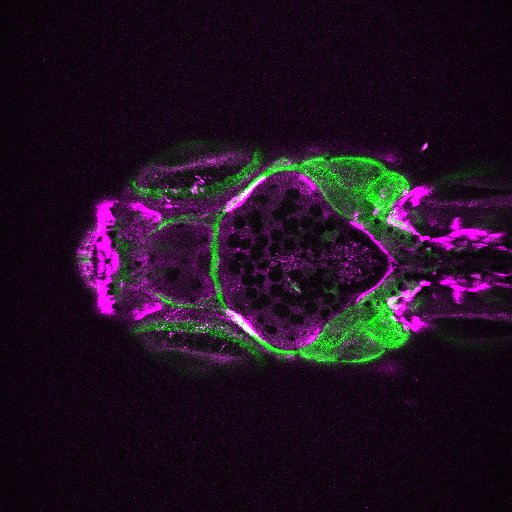
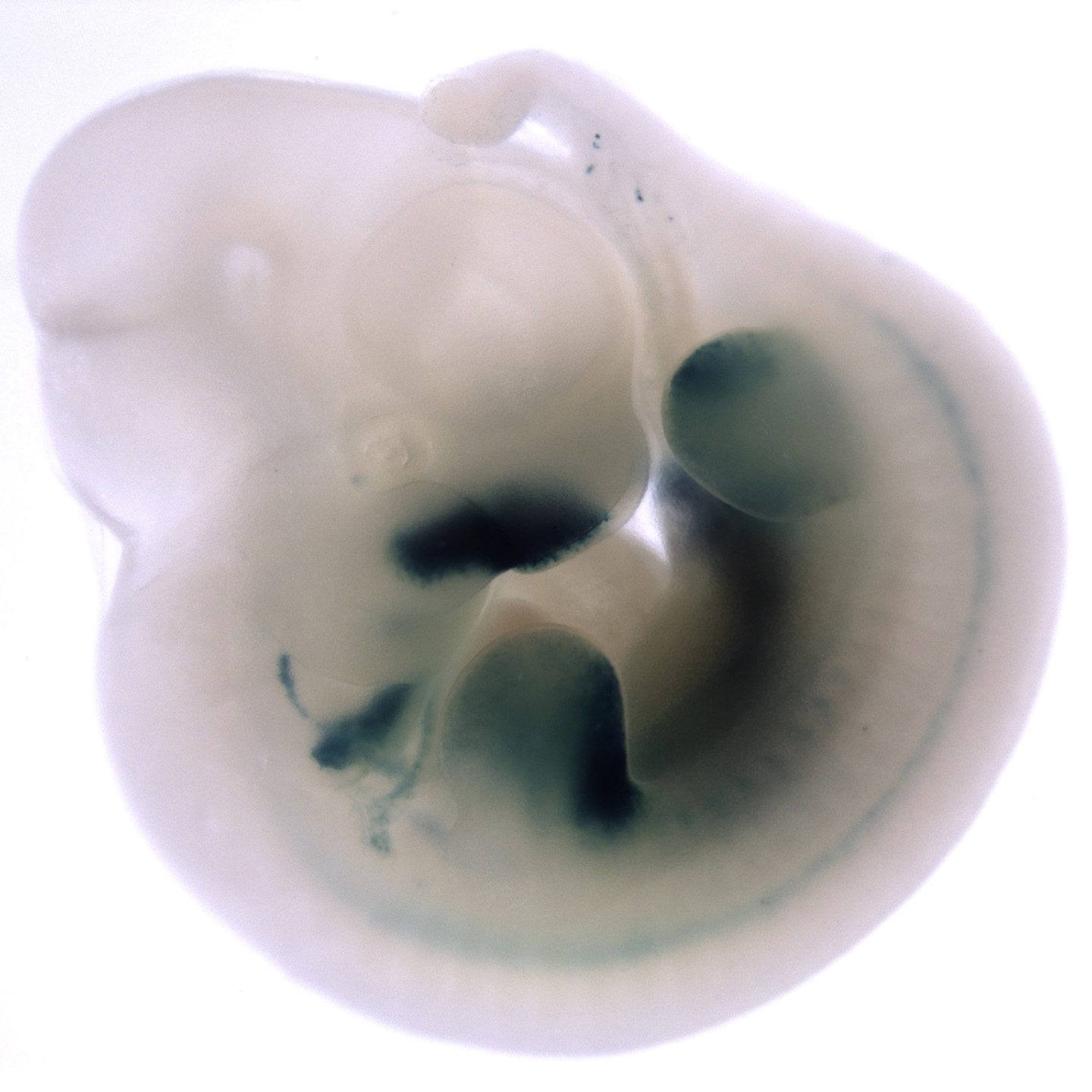
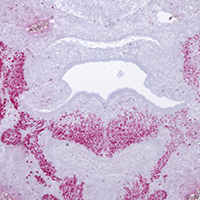
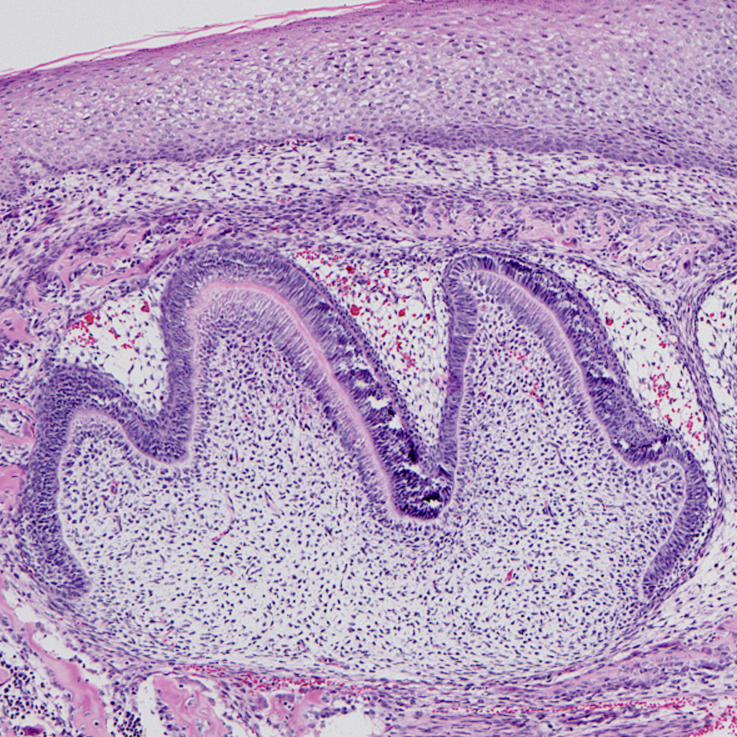
Image Search Below are some examples of the types of imaging data available in FaceBase.
News
- ALL NEWS | SIGN UP FOR OUR MAILING LIST
-
02/11/2026 -
New release: MicroCT analysis of ameloblast specific Smad4 conditional knockout mice and Ambn-IRESCre mouse models
-
02/04/2026 -
Registration and Call for Abstracts Now Open: FaceBase Community Forum 2026
-
01/20/2026 -
New release: Gene expression patterns of the developing face at single cell resolution
-
12/11/2025 -
Save the Date: 2026 FaceBase Community Forum – May 4–5 in Arlington, VA
-
11/10/2025 -
Materials Now Available: November 2025 FaceBase Bootcamp
-
09/18/2025 -
Data release: Identification of lymphatic vessels in skull periosteum but not bone marrow reveals skull channel heterogeneity
Publications
-
Zhu, Hao; Zhang, Jiao; Rao, Soumya; Durbin, Matthew D.; Li, Ying; Lang, Ruirui; Liu, Jiqiang; Xiao, Baichuan; Shan, Hailin; Meng, Ziqiu; Wang, Jinmo; Tang, Xiaokai; Shi, Zhenni; Cox, Liza L.; Zhao, Shouqin; Ware, Stephanie M.; Tan, Tiong Y.; De Silva, Michelle; Gallacher, Lyndon; Liu, Ting; Mi, Jie; Zeng, Changqing; Zheng, Hou-Feng; Zhang, Qingguo; Antonarakis, Stylianos E.; Cox, Timothy C.; Zhang, Yong-Biao. Genome Research. vol. 35(5), 1065–1079. May 2025.
Pathogenic coding variants have been identified in thousands of genes, yet the mechanisms underlying the incomplete penetrance in individuals carrying these variants are poorly understood. In this study, in a cohort of 2009 craniofacial microsomia (CFM) patients of Chinese ancestry and 2625 Han Chinese controls, we identified multiple predicted pathogenic coding variants in SHROOM3 in both CFM patients and healthy individuals. We found that the penetrance of CFM correlates with specific haplotype combinations containing likely pathogenic-coding SHROOM3 variants and CFM-associated expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) of SHROOM3 expression. Further investigations implicate specific eQTL combinations, such as rs1001322 or rs344131, in combination with other significant CFM-associated eQTLs, which we term combined eQTL phenotype modifiers (CePMods). We additionally show that rs344131, located within a regulatory enhancer region of SHROOM3 , demonstrates allele-specific effects on enhancer activity and thus impacts expression levels of the associated SHROOM3 allele harboring any rare coding variant. Our findings also suggest that CePMods may serve as pathogenic determinants, even in the absence of rare deleterious coding variants in SHROOM3 . This highlights the critical role of allelic expression in determining the penetrance and severity of craniofacial abnormalities, including microtia and facial asymmetry. Additionally, using quantitative phenotyping, we demonstrate that both microtia and facial asymmetry are present in two separate Shroom3 mouse models, the severity of which is dependent on gene dosage. Our study establishes SHROOM3 as a likely pathogenic gene for CFM and demonstrates eQTLs as determinants of modified penetrance in the manifestation of the disease in individuals carrying likely pathogenic rare coding variants. -
Mok, Chan Hee; Hu, Diane; Losa, Marta; Risolino, Maurizio; Selleri, Licia; Marcucio, Ralph S.. PLOS Genetics. vol. 21(5), e1011315. May 2025.
Sonic hedgehog (SHH) signaling from the frontonasal ectodermal zone (FEZ) is a key regulator of craniofacial morphogenesis. Along with SHH, pre-B-cell leukemia homeobox (PBX) transcription factors regulate midfacial development. PBXs act in the epithelium during fusion of facial primordia, but their specific interactions with SHH have not been investigated. We hypothesized that PBX1/3 regulate SHH expression in the FEZ by activating or repressing transcription. The hypothesis was tested by manipulating PBX1/3 expression in chick embryos and profiling epigenomic landscapes at early developmental stages. PBX1/3 expression was perturbed in the chick face beginning at stage 10 (HH10) using RCAS viruses, and the resulting SHH expression was assessed at HH22. Overexpressing PBX1 expanded the SHH domain, while overexpressing PBX3 resulted in an opposite effect. Conversely, reducing PBX1 expression decreased SHH expression, but reducing PBX3 induced ectopic SHH expression. We performed ATAC-seq and mapped binding of PBX1 and PBX3 to DNA with ChIP-seq on the FEZ at HH22 to assess direct interactions of PBX1/3 with the SHH locus. These multi-omics approaches uncovered a 400 bp PBX1-enriched element within intron 1 of SHH (chr2:8,173,222–8,173,621). Enhancer activity of this element was demonstrated by electroporation of reporter constructs in ovo and luciferase reporter assays in vitro . When bound by PBX1, this element upregulates transcription, while it downregulates transcription when bound by PBX3. The present study identifies a cis- regulatory element, named SFE1, that interacts with PBX1/3 either directly or within a complex with cofactors to modulate SHH expression in the FEZ. This research establishes that PBX1 and PBX3 play complementary roles in SHH regulation during embryonic development. -
Feng, Jifan; Janečková, Eva; Guo, Tingwei; Ziaei, Heliya; Zhang, Mingyi; Geng, Jessica Junyan; Cha, Sa; Araujo-Villalba, Angelita; Liu, Mengmeng; Ho, Thach-Vu; Chai, Yang. Nature Communications. vol. 16(1), 4396. May 2025.